


The Enhanced ISDN Router (EIR) is a key part of ISDN subsystem in Abilis CPX. ISDN subsystem constists of:
EIR is a smart ISDN telephone exchange. It manages connections among ISDN ports and clusters. As a simplified description we may say that EIR processes an incoming call in following steps: it receives the call request, it finds an appropriate routing, it performs the outgoing call.
EIR supports several types of connection:
Connections can also be:

The Enhanced ISDN Router port is labelled within the Abilis CPX with the acronym "EIR" and it is provided with the parameters described in this section.
Here is an example on how to display the EIR port parameters. Shown values are only examples.
[12:05:12] ABILIS_CPX: D P PO:EIR
PO:200 - Not Saved (SAVE CONF), Not Refreshed (INIT) --------------------------
EIR ------------------------------------------------------------------------
lowpo:100 mxpc:20 +----- EPQ931, EBQ931 and sQ931 ports ----+
ac-buf:5 pl-buf:5 | 296 297 280 281 282 283 . . . . |
Active P-Links : 1 - 8 +-----------------------------------------+
Inactive P-Links: 9 - 64 | . . . . . . . . . . |
+---------- P-Link ports -----------+-----------------------------------+
| PL: ID: MXBW: CURBW: | pl: id: mxbw: curbw: |
|--+--------------------------------|--+--------------------------------|
|1 | 751 TEST1 NOMAX 0 |9 | . . NOMAX N/A |
|2 | 752 TEST2 NOMAX 0 |10| . . NOMAX N/A |
|3 | . . NOMAX . |11| . . NOMAX N/A |
|4 | . . NOMAX . |12| . . NOMAX N/A |
|5 | . . NOMAX . |13| . . NOMAX N/A |
|6 | . . NOMAX . |14| . . NOMAX N/A |
|7 | . . NOMAX . |15| . . NOMAX N/A |
|8 | . . NOMAX . |16| . . NOMAX N/A |
+--+--------------------------------+--+--------------------------------+
To activate any change made on the lowercase parameters, the system has to be started again, on the contrary for the uppercase parameters it is enough to submit the initialisation command INIT PO:.
The "Not Saved (SAVE CONF)" message is displayed every time the port configuration is modified but not saved with the SAVE CONF command.
The "Not Refreshed (INIT)" message is displayed every time the port configuration is modified but not refreshed with the INIT PO: command.
| lowpo: | Identifier of the lower level Abilis CPX port |
| NONE | 1 - 999, NONE |
It sets the lower level port; it can only be the EIM port.
The value "NONE" isolates the EIR port from the lower level ones.
| mxpc: | Maximum number of simultaneous pendent calls |
| 20 | 0 - 255 |
It sets the maximum number of simultaneous calls "under construction", which are also defined "pendent" calls.
![]() If a new call causes to exceed the limit the call will fail immediately, the message "W: MXPC EXCEED" will be written
in the System Log, and an equivalent message will be written in the Debug Log.
If a new call causes to exceed the limit the call will fail immediately, the message "W: MXPC EXCEED" will be written
in the System Log, and an equivalent message will be written in the Debug Log.
![]() Calls in calling or alerting state are pendent calls.
Calls in calling or alerting state are pendent calls.
Calls in connected, disconnecting or releasing state are not pendent calls.
| EPQ931, EBQ931, sQ931 ports: | Lower layer ports |
| NONE | 0 - 999, NONE |
It displays the list of lover level ports.
It is not possible to configure this list manually, it is automatically compiled by the Validation procedure with the
EPQ931, EBQ931 and sQ931 ports, that are configured and active at the moment of its execution.
If the ports are less than 18, the remaining positions are set to "NONE", displayed by the character "." (full stop).
| AC-buf: | Number of buffers used by ACs for jitter compensation |
| 5 | 5 - 50 |
It sets the number of buffers used by Audio Compressors (ACs) for jitter compensation.
The default value of 5 is optimal when packetised voice is carried over leased lines or whenever the jitter is minimal.
For VoIP applications, i.e. when the packetised voice is sent within IP packets over IP networks, and mainly over the Internet,
this value should be increased. Usually a value of 20 provides acceptable results.
![]() Each buffer contains 30 msec of voice, so for each buffer added we increase the jitter compensation of 30 msec.
Each buffer contains 30 msec of voice, so for each buffer added we increase the jitter compensation of 30 msec.
| PL-buf: | Number of transmission buffers used for P-Links |
| 5 | 5 - 50 |
It sets the number of transmission buffers used by P-Links.
The default value of 5 is optimal for all the current applications.
| Active P-Links: | Interval of P-Link ports currently active |
| NONE | 1-8, 1-16, 1-24, 1-32, 1-40, 1-48, 1-56, 1-64 |
This is only an informative parameter and it is not configurable.
It shows the interval of P-Link channels currently active because they were activated at the system start.
This condition is also highlighted by the fact that parameters' tokens, related to the active P-Link group, are displayed in
uppercase.
![]() The parameters of "Active P-Links" can be configured and made active runtime through the INIT PO: command.
The parameters of "Active P-Links" can be configured and made active runtime through the INIT PO: command.
![]() The first 8 P-links are always activated at system start, even if they are not configured.
The first 8 P-links are always activated at system start, even if they are not configured.
| Inactive P-Links: | Interval of P-Link ports currently not-active |
| NONE | 9-64, 17-64, 25-64, 33-64, 41-64, 49-64, 57-64, 0-0 |
This is only an informative parameter and it is not configurable.
It shows the interval of P-Link channels currently inactive because they were not activated at the system start.
This condition is also highlighted by the fact that parameters' tokens, related to the active P-Link group,
are displayed in lowercase.
![]() Parameters' values, eventually configured for those ports, will be activated at the next system start.
Parameters' values, eventually configured for those ports, will be activated at the next system start.
| PL1: - PL64: | PLink lower level port |
| NONE | 0 - 999, NONE |
It shows the P-LINK lower level ports which will transport compressed voice, they can only be MLM ports.
The value "NONE", displayed by the "." character, disables the P-LINK channel.
| ID1: - ID64: | Identifiers of Cluster channels from/to remote EIRs |
| NONE | from 1 up to 8 alphanumerical characters, # |
The EIR port driver uses this parameter value to assign a Cluster identifier to the PLink channel.
The same identifier can be used for more PLink channels, which actually creates a unique Cluster out of several PLink channels. Outgoing compressed call will be routed on these PLinks using a priority scheme, starting from the lower number PLink (e.g. first PL1 until MXBW: is reached or a failure is detected and then PL2).
The value "NONE", configurable by the character "#", is displayed into this table by "." (full stop) and it disables the P-LINK channel.
| MXBW1: - MXBW64: | Maximum bandwidth usable by the correspondent Plink port |
| NOMAX | 0 - 2.048.000, NOMAX |
It sets the maximum bandwidth that compressed voice connections are allowed to use on this PLink.
The value "NOMAX" removes any limit.
![]() A value greater than the actual link capacity may cause voice disruptions when the bandwidth demand actually
exceeds the link capacity.
A value greater than the actual link capacity may cause voice disruptions when the bandwidth demand actually
exceeds the link capacity.
![]() A value very close to the actual link capacity may not leave enough bandwidth for "data services".
However if data service are not multiplexed on the same link this is not a problem.
A value very close to the actual link capacity may not leave enough bandwidth for "data services".
However if data service are not multiplexed on the same link this is not a problem.
| CURBW1: - CURBW64: | Bandwidth currently used by the correspondent PLink port |
| NONE | 0 - 2.048.000, NONE, N/A |
This is only an informative parameter and it is not configurable.
It shows the currently used bandwidth by compressed voice connections on this link.
![]() If one or more connections were established with the "silence compression" feature, instantaneous
values could be lower and the saved bandwidth is instantaneously available for data services.
If one or more connections were established with the "silence compression" feature, instantaneous
values could be lower and the saved bandwidth is instantaneously available for data services.
However the shown value will not flow, actually showing the "maximum bandwidth need".
The value "." means that the PLink channel, even if active, is not working.
The value "N/A" means that the PLink channel was not activated at the system start-up.

How to check state and statistics of the EIR port by the command D S.
[10:49:05] ABILIS-CPX: d s po:EIR
PO:200 ------------------------------------------------------------------------
EIR -- Number of simultaneous calls ----------------------------------------
| State: Alerting/Connected | State: Any |
---------------|---Current---|----Peak-----|---Current---|----Peak-----|
TR | 0| 0| 0| 0|
DATA | 0| 1| 0| 1|
CLUS | 0| 0| 0| 0|
VtoC | 0| 0| 0| 0|
CtoC | 0| 0| 0| 0|
CtoV | 0| 0| 0| 0|
ALL | 0| 1| 0| 1|
------------------------------------------------------------------------
This table shows how many simultaneous connection, of the specified type (TR, DATA,CLUS, VtoC, CtoC, CtoV), the EIR is currently handling (Current), or the peak reached since system start or statistics clearing (Peak).
Connection types are:
| TR | Transparent connection between two ISDN port (voice or data) |
|---|---|
| DATA | Data connection from Abilis CPX to ISDN port or from ISDN port to Abilis CPX |
| CLUS | Dial-up data connection between two CPXs used for compressed voice transfer |
| VtoC | Voice stream from ISDN compressed to packet form sent to cluster |
| CtoC | Compressed voice in packet form from cluster sent to another (or the same) cluster |
| CtoV | Compressed voice in packet from from cluster extracted to voice stream form sent to ISDN port |
| All | Any type of connection. It is important to note that while for "current" connections this field is equal to the sum of all the current connection types, for "peak" connections it represents the peak value of concurrent calls of any type, which is not the sum of individual peaks! |
There are two main pairs of columns:
| State: Alerting/Connected | Number of simultaneous connections in alerting or connected state. |
|---|---|
| State: Any | Numbers of simultaneous connections in any state. |
For each of them there are two sub-columns:
| Current | Number of current simultaneous connections. |
|---|---|
| Peak | Peak value of simultaneous connections reached since system start or statistics clearing. |
How to check the extended and statistics of the EIR port by the command D SE.
[11:08:45] ABILIS-CPX: d se po:EIR
PO:200 ------------------------------------------------------------------------
EIR --- Cleared 000:04:19:32 ago, on 22/03/2002 at 06:49:18 ----------------
-- Number of successful (connected) calls, updated at call end ---------
-----------|---INPUT---|--OUTPUT---|--LOCAL----|--TRANSIT--|----SUM----|
TR | 0| 0| 0| 0| 0|
DATA | 0| 4| 0| | 4|
CLUS | 0| 0| 0| | 0|
VtoC | | 0| | 0| 0|
CtoC | | | | 0| 0|
CtoV | 0| | | 0| 0|
SUM | 0| 4| 0| 0| 4|
------------------------------------------------------------------------
-- Seconds of successful (connected) calls, updated at call end --------
-----------|---INPUT---|--OUTPUT---|--LOCAL----|--TRANSIT--|----SUM----|
TR | 0| 0| 0| 0| 0|
DATA | 0| 508| 0| | 508|
CLUS | 0| 0| 0| | 0|
VtoC | | 0| | 0| 0|
CtoC | | | | 0| 0|
CtoV | 0| | | 0| 0|
SUM | 0| 508| 0| 0| 508|
------------------------------------------------------------------------
-- Number of unsuccessful calls ----------------------------------------
-----------|---INPUT---|--OUTPUT---|--LOCAL----|--TRANSIT--|----SUM----|
TR | 0| 0| 0| 0| 0|
DATA | 0| 0| 0| | 0|
CLUS | 0| 0| 0| | 0|
VtoC | | 0| | 0| 0|
CtoC | | | | 0| 0|
CtoV | 0| | | 0| 0|
SUM | 0| 0| 0| 0| 0|
------------------------------------------------------------------------
-- Internal failures for not connected calls ---------------------------
-----------|---INPUT---|--OUTPUT---|--LOCAL----|--TRANSIT--|----SUM----|
NoRoute | | | | | 0|
NoDest | | | | | 0|
NoPcmRes | 0| 0| 0| 0| 0|
NoAcRes | 0| 0| | 0| 0|
NoHdlcRes | 0| 0| 0| | 0|
PlinkFail | 0| 0| | 0| 0|
ClusFail | 0| 0| | 0| 0|
BwLimit | | 0| | 0| 0|
IsdnL1down | 0| 0| 0| 0| 0|
IsdnL2down | 0| 0| 0| 0| 0|
------------------------------------------------------------------------
-- Internal failures after call connected ------------------------------
-----------|---INPUT---|--OUTPUT---|--LOCAL----|--TRANSIT--|----SUM----|
PlinkFail | 1| 2| | 0| 3|
ClusFail | 0| 0| | 0| 0|
IsdnL1down | 0| 0| 0| 0| 0|
IsdnL2down | 7| 5| 0| 0| 12|
------------------------------------------------------------------------
This table is almost self explaining.
All the counters have the range 0 - 4.294.967.295. They are cleared at system start-up and upon the C S command.
In first three tables there are rows TR, DATA, CLUS, VtoC, CtoC, CtoV indicating the connection type.
It is necessary to explain the columns - INPUT, OUTPUT, LOCAL, TRANSIT - i.e. connection direction.
Each ISDN port has a configuration parameter TYPE:, which can be set to
"USER" or "NETWORK", depending on how we want to consider the port, as a part of the network (NETWORK) or as a part
of the user appliances.
The most common use is to set "NETWORK" for ports connected to the public ISDN network, and "USER" for ports
connected to a PABX or to other user's apppliances.
Please note that a "Cluster port" is always internally set to "NETWORK".
The TYPE: parameter above mentioned is available in the layer 3 driver of the ISDN stack, that is in the Q931/EBQ931/EPQ931 ports.
Connection direction (INPUT, OUTPUT etc.) is evaluated from ISDN ports type:
| LOCAL | Incoming port type is USER, Outgoing port type is USER |
|---|---|
| OUTPUT | Incoming port type is USER, Outgoing port type is NETWORK |
| INPUT | Incoming port type is NETWORK, Outgoing port type is USER |
| TRANSIT | Incoming port type is NETWORK, Outgoing port type is NETWORK |
It is necessary to explain the internal failures of not connected calls:
| NoRoute | EIR received call but no routing in routing table matched |
|---|---|
| NoDest | EIR received call, routing matched but no outgoing port existed |
| NoPcmRes | EIR received call but connection capacity was exhausted |
| NoAcRes | EIR received call but voice compressors were exhausted |
| NoHdlcRes | EIR received call but channels for data via B channel transfer were exhausted |
| PlinkFail | EIR detected a failure on cluster via permanent link |
| ClusFail | EIR detected a failure on cluster |
| BwLimit | EIR reached a bandwidth limit on cluster |
| IsdnL1Down | EIR detected a failure on layer 1 (physical layer) of ISDN stack |
| IsdnL2Down | EIR detected a failure on layer 2 (LAPD) of ISDN stack |
It is also necessary to explain the internal failures after call connection:
| PlinkFail | EIR detected a failure on used cluster via permanent link |
|---|---|
| ClusFail | EIR detected a failure on used cluster |
| IsdnL1Down | EIR detected a failure on layer 1 (physical layer) of ISDN stack of used port |
| IsdnL2Down | EIR detected a failure on layer 2 (LAPD) of ISDN stack of used port |

Voice (fax) interconnection of two offices via ISDN and FR network (VoFR - Voice over Frame Relay)
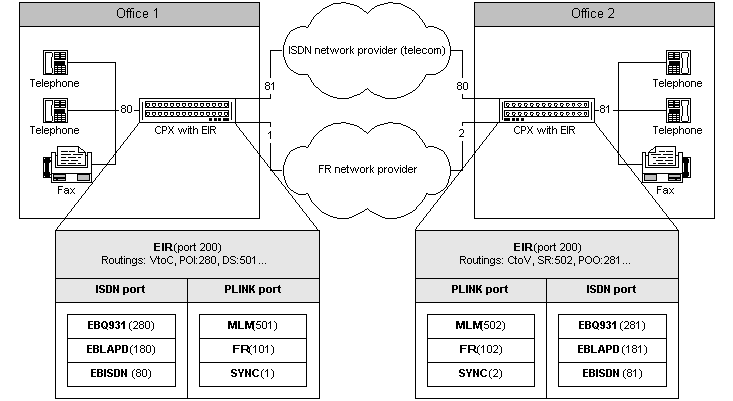
Figure 1. Interconnection of two sites via frame relay and ISDN.
Voice (fax) interconnection of two offices via IP network (e.g. Internet (VoIP - Voice over IP)
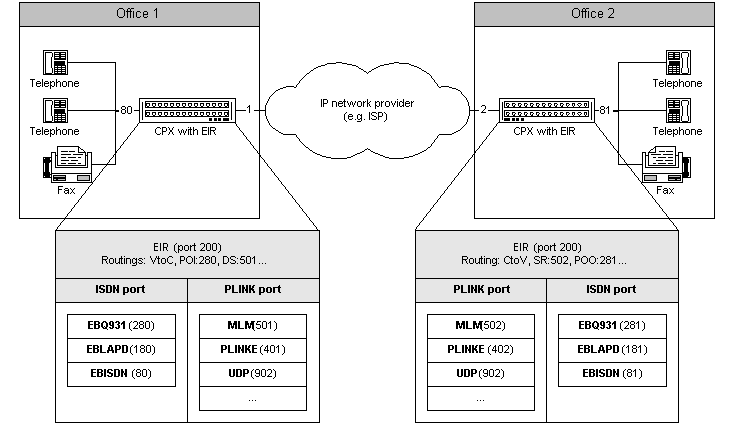
Figure 2. Interconnection of two sites via IP network.